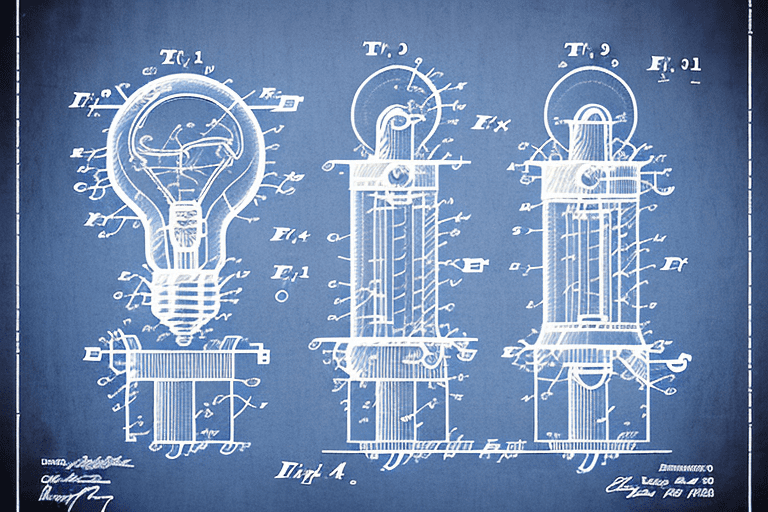
In the world of intellectual property, understanding the terminology is crucial. One term that often comes up is “drawing (patent)”. In this article, we will delve into the concept of patent drawings and its significance in intellectual property.
Understanding Intellectual Property: A Brief Overview
Before we explore patent drawings, let’s take a moment to understand the broader concept of intellectual property (IP). Intellectual property refers to the creations of the mind, such as inventions, artistic works, designs, and symbols. These creations can be protected under various legal frameworks to prevent unauthorized use or duplication.
Intellectual property rights are crucial for both individuals and businesses as they foster innovation, encourage creativity, and provide incentives for investment in research and development.
When it comes to intellectual property, it is essential to recognize its significance in our modern economy. It goes beyond just protecting the rights of creators; it also plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth. Intellectual property provides creators with the exclusive rights to use, sell, or license their inventions, artworks, or designs. This exclusivity ensures that creators can reap the rewards of their efforts.
Moreover, intellectual property rights promote fair competition by preventing others from copying or imitating a product or creation. By safeguarding the original creator’s market share and reputation, intellectual property rights create a level playing field for businesses and encourage them to invest in research and development.
The Importance of Intellectual Property
IP rights not only protect the interests of creators but also benefit society as a whole. By granting exclusive rights to creators, intellectual property laws encourage them to share their knowledge and inventions with the public. This sharing of ideas fosters innovation, as others can build upon existing knowledge to create new and improved products or technologies.
Furthermore, intellectual property rights provide a framework for collaboration and licensing agreements. Creators can license their intellectual property to others, allowing for the development of new products and technologies through partnerships and cross-industry collaborations.
Different Types of Intellectual Property
There are several types of intellectual property, each with its own set of rules and regulations. Understanding the different categories is essential for creators and businesses to protect their creations effectively. The main categories include:
- Patents: These protect inventions, processes, and discoveries. Patents provide inventors with exclusive rights for a limited period, enabling them to commercialize their inventions and prevent others from using or selling their patented technology without permission.
- Trademarks: These protect brand names, logos, and symbols. Trademarks help businesses establish and protect their brand identity, ensuring that consumers can identify and distinguish their products or services from those of competitors.
- Copyrights: These protect original artistic and literary works. Copyrights give creators exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, display, perform, and create derivative works based on their original creations.
- Trade Secrets: These safeguard confidential business information. Trade secrets include formulas, processes, methods, or any valuable information that gives a business a competitive advantage. Unlike patents, trade secrets do not require registration and can be protected indefinitely as long as they remain confidential.
- Industrial Designs: These protect the aesthetic features of a product. Industrial designs cover the visual appearance of a product, including its shape, pattern, or color. This type of intellectual property protection is particularly important in industries where the design plays a significant role in attracting consumers.
Now that we have a better understanding of intellectual property and its various forms, let’s delve into the fascinating world of patent drawings. Patent drawings are an essential part of the patent application process, providing visual representations of an invention that complement the written description.
The Concept of Patent Drawings
At its core, a patent drawing is a visual representation of an invention or design that is submitted as part of a patent application. These drawings serve as valuable supporting material, complementing the written description of the invention.
Defining Patent Drawings
In simple terms, patent drawings are visual tools used to clearly depict an invention or design. They illustrate the features, functions, and structure of the invention in a way that words alone cannot convey.
Patent drawings can range from basic sketches to highly detailed technical illustrations, depending on the complexity of the invention. These drawings must meet certain requirements to fulfill their purpose effectively.
When creating patent drawings, it is important to consider various factors, such as the level of detail required, the specific guidelines set by the patent office, and the target audience of the patent application. These considerations will help ensure that the drawings effectively communicate the essence of the invention.
The Role of Patent Drawings in Intellectual Property
Patent drawings serve several crucial purposes in the field of intellectual property:
- Enhancing Clarity: Drawings clarify complex technical concepts and provide a visual aid for understanding the invention. By visually representing the invention, patent drawings can help bridge the gap between the language of the patent application and the practical implementation of the invention.
- Supporting Claims: Drawings help support the claims made in the patent application, highlighting the unique and innovative aspects of the invention. By visually demonstrating the features and functions of the invention, patent drawings can provide additional evidence to strengthen the claims.
- Facilitating Examination: Patent examiners rely on drawings to assess the patentability of an invention, comparing it with existing prior art. By examining the drawings, patent examiners can better understand the technical details of the invention and evaluate its novelty and non-obviousness.
Now that we understand the importance of patent drawings, let’s explore the essential elements that make up an effective drawing.
When creating patent drawings, it is crucial to include accurate and detailed representations of the invention. This includes capturing the various components, structures, and configurations of the invention in a clear and concise manner. Additionally, it is important to use appropriate shading, line thickness, and labeling to enhance the clarity and understanding of the drawings.
Furthermore, it is essential to follow the specific guidelines provided by the patent office regarding the format, size, and resolution of the drawings. These guidelines ensure consistency and standardization across patent applications, making it easier for patent examiners and other stakeholders to review and analyze the drawings.
In conclusion, patent drawings play a vital role in the patent application process. They provide a visual representation of the invention, enhancing clarity, supporting claims, and facilitating examination. By following the guidelines and incorporating the essential elements, patent drawings can effectively communicate the essence of the invention and increase the chances of obtaining a valuable patent.
Essential Elements of a Patent Drawing
A well-crafted patent drawing incorporates several key elements to effectively convey the invention. Let’s take a closer look:
Detailed Description
One of the fundamental requirements of a patent drawing is to provide a detailed description of the invention. This description should clearly explain the structure, components, and operation of the invention, leaving no room for ambiguity.
Through detailed descriptions, patent drawings facilitate a deeper understanding of the invention and its innovative features. For example, if the invention is a new type of engine, the detailed description may include information on the engine’s design, fuel consumption, power output, and any unique features that set it apart from existing engines.
Furthermore, the detailed description may also delve into the technical specifications of the invention, such as dimensions, materials used, and any specific manufacturing processes involved. This level of detail ensures that anyone reading the patent drawing can fully grasp the intricacies of the invention.
Multiple Views
An effective patent drawing should provide multiple views of the invention. These multiple views ensure that all aspects of the invention are adequately captured, including different angles, cross-sections, and exploded views if necessary.
By including multiple views, patent drawings allow for a comprehensive understanding of the invention’s physical appearance and structure. For instance, if the invention is a complex electronic device, the patent drawing may provide front, side, and top views, as well as internal views to showcase the arrangement of components and circuitry.
These multiple views not only aid in understanding the invention but also serve as a valuable resource for manufacturers and engineers who may need to replicate or improve upon the invention in the future.
Reference Numbers
To enhance clarity and avoid confusion, reference numbers are often used in patent drawings. These numbers are labels or callouts that correspond to specific parts or components of the invention.
By using reference numbers, patent drawings create a clear and consistent framework for identifying and discussing different elements of the invention. For example, if the invention is a new type of bicycle, the patent drawing may include reference numbers for the wheels, frame, handlebars, pedals, and other relevant parts.
These reference numbers not only make it easier to refer to specific components in the detailed description but also enable patent examiners and interested parties to quickly locate and understand different aspects of the invention without any confusion.
In conclusion, a well-crafted patent drawing incorporates a detailed description, multiple views, and reference numbers to effectively convey an invention. These elements ensure that the invention is thoroughly understood and properly protected, allowing innovators to showcase their creativity and contribute to the advancement of technology.
How to Create Effective Patent Drawings
Creating effective patent drawings requires adherence to specific guidelines set by the patent office. Here are some key considerations:
Understanding the Patent Office Requirements
Before diving into the drawing process, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the patent office where you plan to file your application. Each office may have its own rules regarding the format, style, and quality of drawings.
By understanding these requirements in advance, you can ensure that your drawings meet all necessary criteria for acceptance.
Tips for Creating Clear and Detailed Drawings
When creating patent drawings, clarity and detail are of utmost importance. Here are some tips to help you create drawings that effectively convey your invention:
- Use professional drafting tools or computer-aided design (CAD) software for precise lines and dimensions.
- Ensure that your drawings are legible and use appropriate scales to accurately represent the invention.
- Label all components clearly using reference numbers and provide a comprehensive legend or key.
By following these tips, you can create drawings that not only satisfy the requirements but also showcase your invention in the best possible light.
Common Mistakes in Patent Drawings and How to Avoid Them
Creating patent drawings can be a complex task, and it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls. Let’s explore some common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Inadequate Detailing
One of the most significant mistakes in patent drawings is insufficient detailing. Lack of clarity, imprecise labeling, or incomplete representation of the invention can hinder understanding and jeopardize the patent application’s success.
To avoid this mistake, ensure that your drawings provide a clear, comprehensive, and accurate representation of the invention, leaving no room for ambiguity.
Non-compliance with Patent Office Standards
Each patent office has its own set of rules and standards for patent drawings. Failing to adhere to these standards can result in rejection or delay in the patent application process.
Thoroughly review the guidelines provided by the patent office and consult professional draftspeople or patent attorneys for assistance in complying with these standards.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can significantly enhance the quality and effectiveness of your patent drawings.
In conclusion, patent drawings play a crucial role in intellectual property by providing a visual representation of inventions and designs. Understanding the requirements and elements of effective patent drawings is essential for protecting and showcasing innovative ideas. By adhering to the guidelines and investing in precise and detailed drawings, inventors can increase their chances of securing the intellectual property rights they deserve.