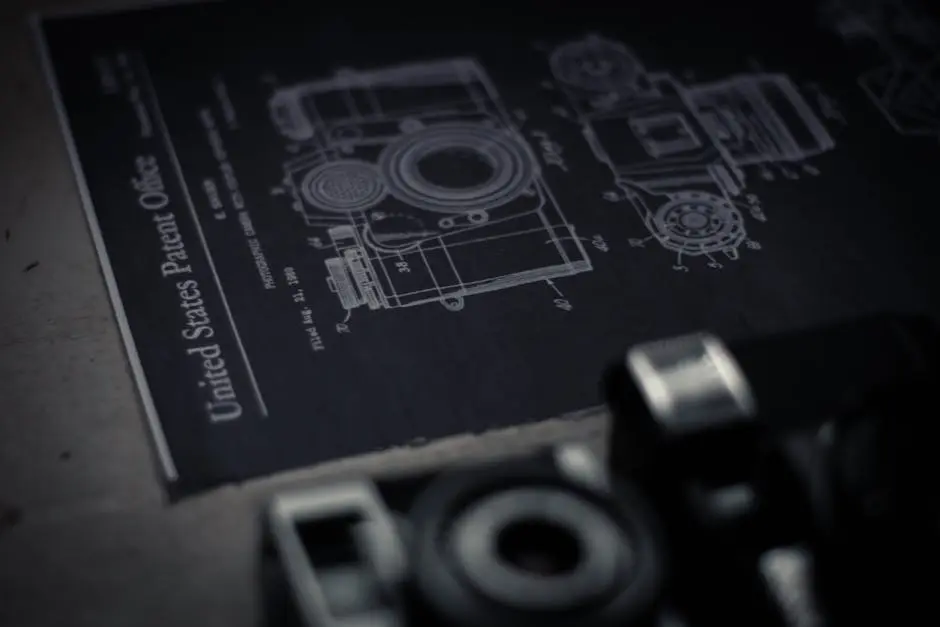
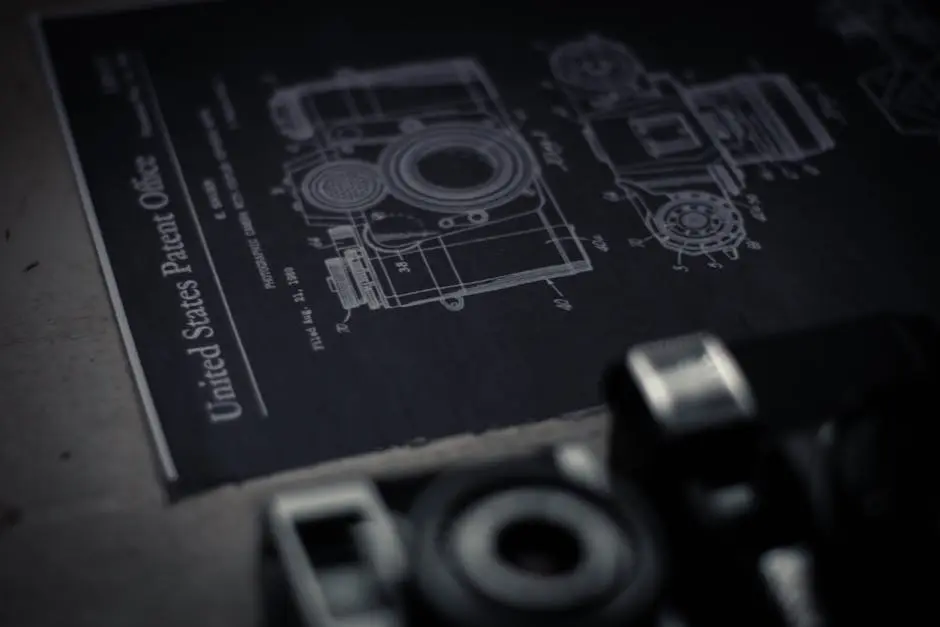
Introduction to Intellectual Property Law
In today’s rapidly evolving world, understanding intellectual property law is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Intellectual property law protects creations of the mind, providing legal rights to inventors, artists, and businesses for their innovations and creations. As we navigate through 2026, the significance of intellectual property law continues to grow, influencing various sectors from technology to entertainment. This article will delve into the intricacies of intellectual property law, offering insights into its types, importance, and practical applications.
Key Takeaways
– Intellectual property law safeguards creations of the mind, enhancing innovation.
What is Intellectual Property Law?
Intellectual property law encompasses the rules and regulations designed to protect the rights of creators for their intellectual efforts. It grants creators exclusive rights to use and exploit their creations, ensuring they can benefit financially and gain recognition.
Types of Intellectual Property
Patents: Protecting Innovations
Patents are legal rights granted to inventors for their unique inventions. They prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention without permission. Patents are crucial in fostering innovation by giving inventors the incentive to invest time and resources into developing new technologies. In 2026, patents remain a cornerstone in sectors like pharmaceuticals and technology, where research and development are pivotal.
How Do Patents Work?
A patent provides the inventor with the exclusive right to exploit their invention. This exclusivity is time-limited, usually lasting 20 years from the filing date. To obtain a patent, the inventor must disclose the invention in a patent application, which is reviewed by a patent office. If granted, the patent application becomes a public document, detailing the invention and its uses.
Types of Patents
There are three main types of patents: utility patents, design patents, and plant patents. Utility patents are the most common, covering new and useful inventions or discoveries. Design patents protect the unique visual qualities of an object, while plant patents cover new, distinct plant varieties. Each type serves a different purpose, catering to various aspects of innovation.
Challenges in Patent Law
Despite their importance, obtaining and enforcing patents can be challenging. The application process is complex, often requiring detailed technical descriptions and legal expertise. Additionally, patent infringement cases can be costly and time-consuming. For aspiring patent practitioners, courses like Wysebridge Patent Bar Review offer invaluable guidance, helping candidates prepare for the USPTO Patent Bar Exam with tailored study plans and expert support.
Trademarks: Branding and Identity
Trademarks protect symbols, names, and slogans used to identify goods or services. They play a vital role in brand recognition and consumer trust. In 2026, with the rise of digital marketing, trademarks have become more important than ever in distinguishing products in a crowded marketplace.
The Role of Trademarks in Business
Trademarks help businesses establish a unique identity, differentiating their products from competitors. A strong trademark can enhance brand loyalty, making it a valuable asset. Companies invest significantly in trademark development and protection, recognizing its impact on market positioning and consumer perception.
Trademark Registration Process
To register a trademark, businesses must file an application with the relevant trademark office. The application should include a clear representation of the mark and a list of goods or services it will cover. Once registered, the trademark owner can use the ® symbol, signaling legal protection.
Common Trademark Issues
Trademark disputes often arise from similarities between marks, leading to consumer confusion. Companies must conduct thorough searches before filing applications to avoid conflicts. Additionally, maintaining trademark rights requires active use and monitoring to prevent unauthorized use by others.
Copyrights: Protecting Creative Works
Copyrights safeguard original works of authorship, such as literature, art, music, and software. They grant creators the exclusive right to use and distribute their works, encouraging creativity and cultural enrichment.
How Copyrights Work
Copyright protection is automatic upon the creation of an eligible work, requiring no formal registration. However, registering a copyright with the relevant office provides additional legal benefits, such as the ability to sue for infringement in federal court.
Copyright Duration and Limitations
In 2026, the duration of copyright protection lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years. For corporate works, the term is 95 years from publication or 120 years from creation, whichever is shorter. Despite these protections, certain limitations exist, such as fair use, which allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research.
Digital Copyright Challenges
The digital era presents unique challenges for copyright enforcement. Online piracy and unauthorized distribution are prevalent, requiring creators to employ digital rights management (DRM) and other technological measures to protect their works.
Trade Secrets: Protecting Confidential Information
Trade secrets encompass confidential business information that provides a competitive edge. Unlike other intellectual property types, trade secrets are not registered; their protection relies on maintaining secrecy.
Importance of Trade Secrets
Trade secrets are vital for businesses, as they include formulas, practices, processes, designs, instruments, or compilations of information that are not generally known. They can range from manufacturing processes to customer lists and marketing strategies.
Protecting Trade Secrets
To safeguard trade secrets, companies implement strict confidentiality agreements and security measures. Employees and partners are required to sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to prevent unauthorized disclosure.
Legal Framework for Trade Secrets
In the U.S., trade secrets are protected under the Defend Trade Secrets Act (DTSA) and state laws. These laws provide remedies for misappropriation, including injunctions and damages. However, proving misappropriation can be challenging, necessitating detailed documentation and evidence.
The Importance of Intellectual Property Law
Fostering Innovation and Creativity
Intellectual property law incentivizes innovation by granting creators exclusive rights to their inventions and works. This exclusivity encourages investment in research and development, driving technological advancements and cultural enrichment.
Economic Impact of Intellectual Property
Intellectual property-intensive industries contribute significantly to the economy, generating jobs and driving economic growth. In 2026, these industries account for a substantial portion of GDP, highlighting the economic importance of intellectual property protection.
Balancing Rights and Public Access
While intellectual property law protects creators, it also balances their rights with public access. Laws like fair use and compulsory licensing ensure that essential knowledge and cultural works remain accessible, promoting societal progress.
Global Perspectives on Intellectual Property
International treaties, such as the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), harmonize intellectual property laws across countries. These agreements facilitate global trade and cooperation while respecting cultural differences.
Intellectual Property and the Digital Age
The Rise of Digital Platforms
The digital age has transformed how intellectual property is created, shared, and protected. Platforms like social media and streaming services have revolutionized content distribution, necessitating new approaches to intellectual property management.
Challenges in the Digital Landscape
Digital platforms pose unique challenges for intellectual property enforcement. Unauthorized sharing, counterfeiting, and piracy are rampant, requiring innovative solutions and international cooperation to combat these issues.
Technological Solutions for IP Protection
Technology plays a crucial role in protecting intellectual property in the digital age. Blockchain, artificial intelligence, and digital watermarking are among the tools used to enhance security and traceability of digital assets.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Intellectual Property Law
As we advance through 2026, the relevance of intellectual property law continues to grow, influencing various aspects of our lives. Understanding and effectively navigating intellectual property law is essential for creators, businesses, and consumers alike. By fostering innovation and protecting valuable assets, intellectual property law plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of industries worldwide. Whether you are an aspiring patent practitioner or a business owner, leveraging resources like Wysebridge Patent Bar Review can provide you with the insights and expertise needed to succeed in the complex world of intellectual property.
FAQs about Intellectual Property Law
What is the main purpose of intellectual property law?
Intellectual property law aims to protect the rights of creators and inventors by granting them exclusive rights to their creations.
How long does a patent last?
A patent typically lasts 20 years from the filing date, providing the inventor with exclusive rights to their invention during this period.
What is the difference between a copyright and a trademark?
Copyrights protect original works of authorship, while trademarks protect symbols, names, and slogans used to identify goods or services.
Can trade secrets be registered?
No, trade secrets are not registered. Their protection relies on maintaining confidentiality and security measures.
Why is intellectual property important for businesses?
Intellectual property is crucial for businesses as it protects their innovations and brand identity, providing a competitive edge in the market.
How does digital technology impact intellectual property law?
Digital technology presents challenges and opportunities for intellectual property law, requiring new approaches to protect and manage digital assets.